Reliable and consistent backup of cloud data is important to have a secure data archive and restore in the event of data loss. Traditionally, backup administrators used manual backup procedures that were difficult to scale and lowered productivity, with data distributed across multiple cloud resources. Cloud backup, along with the automation of infrastructure provisioning, are prompting organizations to improve their data protection and backup strategy.
Customers are implementing infrastructure as code (IaC) as an essential part of their digital transformation to improve productivity and govern infrastructure operations across multi-account environments. Implementing backup policies as code can help you scale your enterprise data protection strategy, reduce overhead, and easily manage organization-wide policies at scale across your cloud environment. AWS Backup offers a cost-effective, fully managed, policy-based managed service that simplifies data protection at scale. AWS Backup leverages AWS Organizations to centrally automate backup policies to implement, configure, manage, and govern backup activity across supported AWS resources.
In previous blog posts, our colleague Cher covered how AWS Backup can simplify centralized backup management with Cross-Region copy and secure data recovery with cross-account, cross-Region backup by implementing backup policies using the AWS Backup console. In this blog post, we demonstrate how you can save time using AWS CloudFormation automation to centrally automate and scale the process of implementing AWS Backup policies, backup vaults, and cross-Region, cross-account replication across your multi-account AWS environment. Using this solution, you can easily manage AWS Backup with automation and implement a data protection strategy that mitigates the risk of data loss.
Solution overview
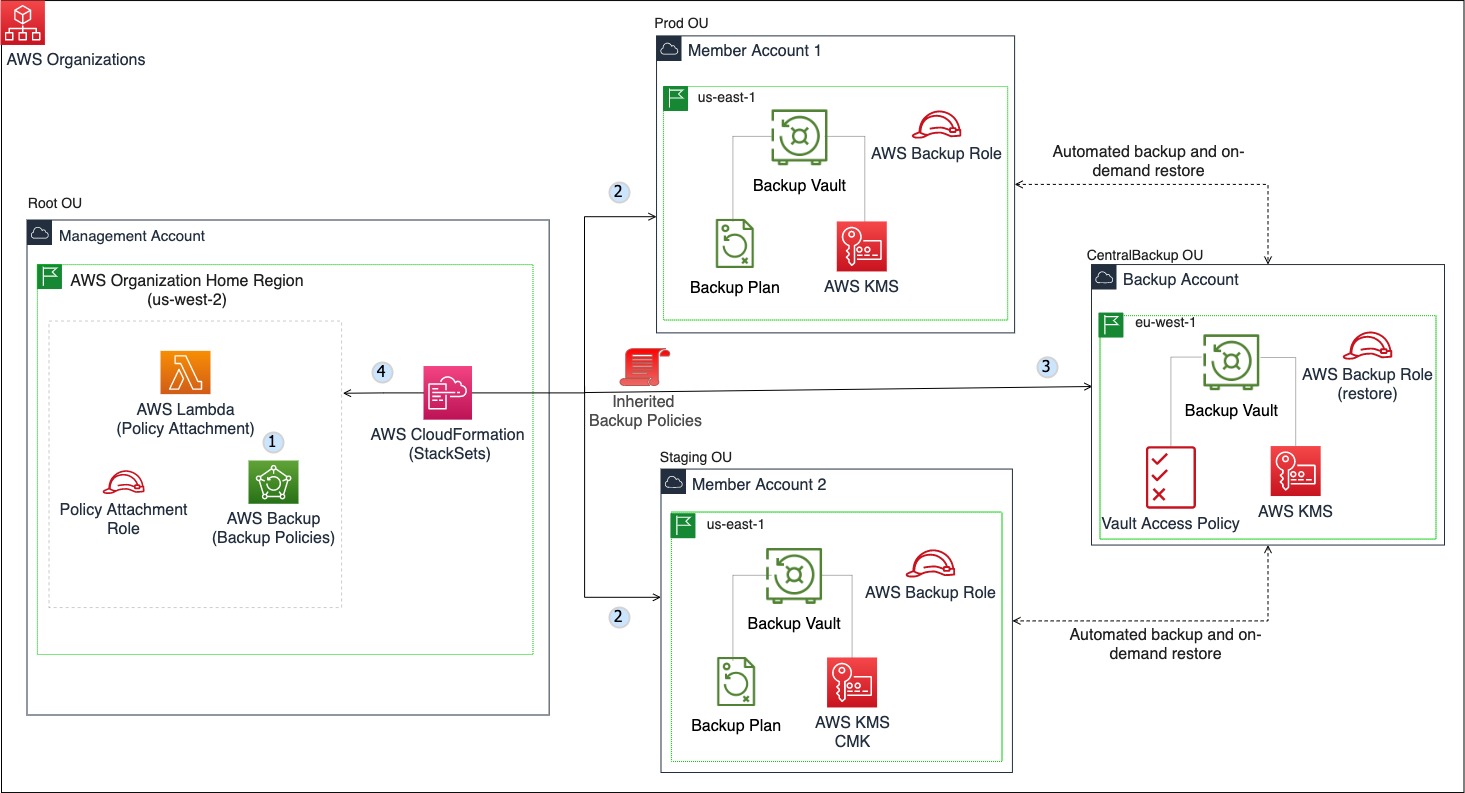
The architecture uses AWS Control Tower and consists of four AWS Organizations accounts: a management account, two member accounts, and a centralized backup account that belong to their respective organizational units. AWS Organizations helps to centrally manage, govern, automate, and scale AWS resources across accounts in an organization. The solution uses AWS CloudFormation stacks and StackSets to deploy resources such as backup vaults, vault access policies, AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) customer managed keys (CMK), and IAM roles.
AWS Backup policies define how you back up your resources using backup plans. Backup policies are written in plaintext files and structured according to the JSON rules. You can attach a backup policy to any elements of your organization’s hierarchy such as AWS accounts or organizational unit (OU). The backup policy specifies the final backup plan settings that apply to an AWS account within the organization. To facilitate the inheritance of effective backup policy in our solution, we attach the backup policies to the Root OU using an AWS Lambda function. We also leverage tags to add AWS resources in each member account to the backup policies.
A successful deployment of this solution can help you perform automated backups using centralized backup policies across your organization. You can conduct on-demand restore operation across your member accounts.
The following diagram illustrates the AWS Backup automation solution discussed in this blog:

The workflow and architecture of the solution works as follows:
In the management account (the environment hosting your AWS Organizations):
- Opt in to use the AWS Backup service and cross-account management features.
- The first stackset implements the local backup vaults, IAM roles, and vault AWS KMS encryption keys in member accounts 1 and 2. We assume that the supported AWS Backup resources in the member accounts are tagged as indicated in the prerequisites section of this blog.
- The second stackset implements the central backup vault, IAM role, vault AWS KMS encryption key, and vault access policy in the backup account.
- Finally, we deploy a stack to implement a Lambda function, Lambda IAM role, and centralized backup policies. The backup policies consist of tag-based and cross-account, cross-Region copy policies that are automatically attached to the root OU and inherited by all AWS Organizations accounts.
The source code for this blog can be downloaded from this GitHub repository.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to deploy the solution.
- You must have four accounts that belong to the same AWS Organizations (see the documentation on AWS Organizations). We assume you have placed the accounts in an organization hierarchy.
- AWS Organizations root ID, account ID, and organization ID can be found in the AWS Organizations console. See the AWS Organizations documentation for further details.
- Set up a supported resource such as Amazon EBS volume in the member accounts to demonstrate the backup functionality. Tag each of your EBS volumes; you can use “project” for key and “aws-backup-demo” for value, or “environment” for key and “aws-dev” as value. See the documentation on creating an Amazon EBS volume for more information.
- Basic knowledge of CloudFormation StackSets, Lambda functions, and Python.
- Install latest version of the AWS CLI or use the AWS CloudShell. To use the AWS CLI, you must make sure that you have profiles with credentials for the management account configured in ~/.aws/credentials and ~/.aws/config files. You can get more information about creating CLI configuration files in the AWS CLI user guide.
Walkthrough
Complete the following steps to implement this solution:
Step 1: Opt in to use AWS Backup
If this is your first time using the AWS Backup service, you must opt in to use AWS Backup and cross-account management features using the AWS Management Console or CLI.
To opt in using AWS Management Console (recommended):
- Open the AWS Backup console in your management account and from the left navigation pane, choose Settings, and then choose Enable for Backup policies, Cross-account monitoring, and Cross-account backup.
- The status of the cross-account management settings would change to Enabled.
- Ensure that you have enabled your supported workloads in the Service opt-in
You can refer to the existing AWS Backup blog on cross account, cross-Region backup for additional help with using the AWS Management Console for service opt-in.
To opt in using AWS CLI or CloudShell:
- Open the configured AWS CLI or CloudShell to access your management account and run the following command:
aws organizations enable-policy-type --root-id r-<examplerootid>
--policy-type BACKUP_POLICY
aws organizations enable-aws-service-access --service-principal
backup.amazonaws.com
aws backup update-global-settings --global-settings
isCrossAccountBackupEnabled=true

- The status of the cross-account management settings should change to Enabled.
Step 2: Deploy member account resources
In this step, you deploy cross-account IAM roles, backup vaults, a KMS key to encrypt backup vaults, and a vault access policy to all member accounts using AWS CloudFormation StackSets. Complete the following steps to create the backup resources, and implement secure vault access policy in each of your member accounts. If you want to read more about CloudFormation StackSets, see the blog post on using AWS CloudFormation StackSets for multiple accounts in an AWS Organization.
- Log in to your management account and select the appropriate AWS Region.
- Navigate to the AWS CloudFormation StackSets console in the AWS Region being used, and create a new stackset using the
aws-backup-member-account.yamltemplate. - Enter the StackSet name. In our example, we use
Backup-Member-Accounts. Under the Parameters section, enter values for the following parameters:- pCrossAccountBackupRole: This is the IAM role name for the cross-account backup role that carries out the backup activities.
- pBackupKeyAlias: This is the name of the AWS Backup KMS key alias.
- pMemberBackupVaultName: This is the name of the member account backup vaults.
- pOrganizationId: This is the AWS Organization ID value.
- pTagKey1: This is the tag key to assign to resources.
- pTagValue1: This is the tag value to assign to resources.

- On the Permissions section, select the Self-service permissions. We choose the following settings:
- IAM role name:
AWSControlTowerStackSetRole - IAM execution role name:
AWSControlTowerExecution
- IAM role name:

- On the Set deployment options, choose Deploy stacks in accounts and provide a comma-separated list of AWS account numbers for the member accounts. On the Specify Regions section, select the AWS Regions where you want to deploy the member account’s vault and resources from the drop-down list.
- On the Review page, validate the parameters and check the box I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resource with custom names. Then select Submit.
- On the Stack Instances, validate the stackset deployment and wait for the status to change from an OUTDATED to a CURRENT stack instance.
For more information, see the documentation on creating a stack set.
Step 3: Deploy centralized backup account resources
This step is the same as step 2 in the preceding section, but here you will deploy resources to the centralized backup account and include additional parameter values in the StackSet. Complete the following steps to create the backup resources that you will use for cross-account and cross-Region data replication.
- Repeat steps 1–7 from step 2 using the CloudFormation template
aws-backup-central-backup-account.yaml. - The following are additional parameters required for this step:
- pCentralBackupVaultName: This is the name of the centralized account backup vault.
- pMemberOneAccountId: This is the account ID of the first member account.
- pMemberTwoAccountId: This is the account ID of the second member account.
Step 4: Deploy the management account resources
In the previous steps, you implemented automation to set up backup vaults, KMS keys, IAM roles, and vault access policies. Now, you create custom backup policies applicable to your organization and set up the management account to automate the deployment of the policies. The management account attaches the backup policies to specified AWS accounts or organizational units using an AWS Lambda function hosted in Amazon S3.
Important Note: When you upload a Lambda function’s deployment package from an Amazon S3 bucket, the bucket must be in the same Region as the function. If the OrgPolicyCustomResourceManager.zip file is stored in an S3 bucket that is in a different Region as the Lambda function, you may get the following error:
Error occurred while GetObject. S3 Error Code: PermanentRedirect. S3 Error Message: The bucket is in this region: <aws-region>. Please use this region to retry the request.
To prevent this error, ensure you create a deployment artifact bucket for each Region where you deploy the Lambda code. If you want to read more about this note, see the documentation on Troubleshooting AWS Lambda deployments.
The following code snippet shows a section of a tag-based backup policy with TAG_KEY_2 and TAG_VALUE_2 used as tag identifiers to automatically assign resources to a backup plan. The snippet leverages the BACKUP_ROLE to initiate the backup. To read more about the syntax, see the documentation on AWS Backup Policy syntax and examples for additional information.
"selections": {
"tags": {
"OrgDailyBackupSelection": {
"iam_role_arn": {
"@@assign": "arn:aws:iam::$account:role/BACKUP_ROLE",
},
"tag_key": {
"@@assign": "TAG_KEY_2"
},
"tag_value": {
"@@assign": [
"TAG_VALUE_2"
]
},
},
},
},To deploy the backup policy automation:
- Customize the backup policy section (rOrgBackupPolicy) of the CloudFormation template in
aws-backup-org-policy.yamlto include your custom backup windows, copy actions, central account backup vault ARN, backup plan tag value (backup_plan_tags), recovery point tag value (recovery_point_tags), lifecycle policies, etc. For more information, see the sample backup policies in the official documentation. - Navigate to the AWS CloudFormation Stack console in the AWS Region being used. Create a new CloudFormation Stack using the CloudFormation template. Enter the Stack name.
- The following are additional parameters required for this step:
- pOrgbackupAccounts: A CSV list of the AWS account id or AWS Organizations OU id to attach backup policies. In our example, we attached the policies to the ‘Root OU id’ denoted by r-<example-root-id>.
- pLambdaS3BucketName: The name of the S3 bucket hosting the custom Lambda code. By default, the Lambda code is hosted by AWS in the ‘awsstorageblog’ bucket.
- pCrossAccountBackupRole: This is the IAM role name for the cross-account backup role carries out the backup activities.
- pBackupScheduler: The CRON job to initiate backup tasks. For example: cron(0 0/1 ? * * *). See the documentation on backup schedule expression for further details.
- pMemberAccountBackupVault: The name of the member account Backup vaults. (Name is case sensitive).
- pBackupTagKey1: The backup tag key 1 to automatically assign resources to a backup plan across the member accounts. Your BackupTagKey and BackupTagValue should be equal to the tags you assign to your cloud resources.
- pBackupTagValue1: The backup tag value 1 to automatically assign resources to a backup plan across the member accounts.
- pBackupTagKey2: The backup tag key 2 to automatically assign resources to a backup plan across the member accounts.
- pBackupTagValue2: The backup tag value 2 to automatically assign resources to a backup plan across the member accounts.

- On the Review page, validate the parameters and check the box I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resource with custom names. Then select Submit.
- On the Stack Events, validate the stack deployment and wait for the status to change from IN PROGRESS to CREATE COMPLETE.
You have successfully implemented AWS Backup with automated backup policies and cross-account, cross-Region copy.
Monitor AWS Backup
All the AWS Backup policies and the jobs associated with those policies can be monitored using the cross-account monitoring capabilities in the management account. For detailed instructions on how to view and manage AWS Backup jobs, see the documentation on monitoring activities in multiple AWS accounts.
Cleaning up
To avoid incurring future charges, delete the resources. First, Delete the stack instances, then delete the StackSets from the AWS CloudFormation console.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we showed you how to implement backup policies as code to help you scale your data protection strategy, reduce overhead, and manage organization-wide backup policies. We demonstrated how to apply your backup policies from a central management account to effectively back up and manage resources across your member accounts.
eliable and consistent backup of cloud data is important to have a secure data archive and restore in the event of data loss.
Backing up data is an essential part of most data management strategies, and backup requirements are often driven through organization or regulatory requirements. With secure and reliable backups, you can be ready in the event event of unexpected data loss to restore your data. The solution covered in this post allows you to automate and easily manage your backup plans at scale, across your cloud workloads. Through automation, you can avoid manual and time-consuming backup procedures that can lower your organizational efficiency and make managing backups more difficult.
To get started on AWS or to learn more about building a well-architected AWS environment, visit the getting started with AWS Backup page for guidance.
Thank you for reading this blog. If you have any feedback or questions, please leave them in the comments section.